
- #HOW TO SAVE A FILE IN .TIF FORMAT IN MICROSOFT ON MAC PDF#
- #HOW TO SAVE A FILE IN .TIF FORMAT IN MICROSOFT ON MAC PC#
- #HOW TO SAVE A FILE IN .TIF FORMAT IN MICROSOFT ON MAC FREE#
All labeling and annotation should be performed without obscuring any data or background bands.

Molecular weight markers should be included or indicated on the raw image, and any lanes not included in the final figure should be marked with an “X” above the lane label on the original blot/gel image.
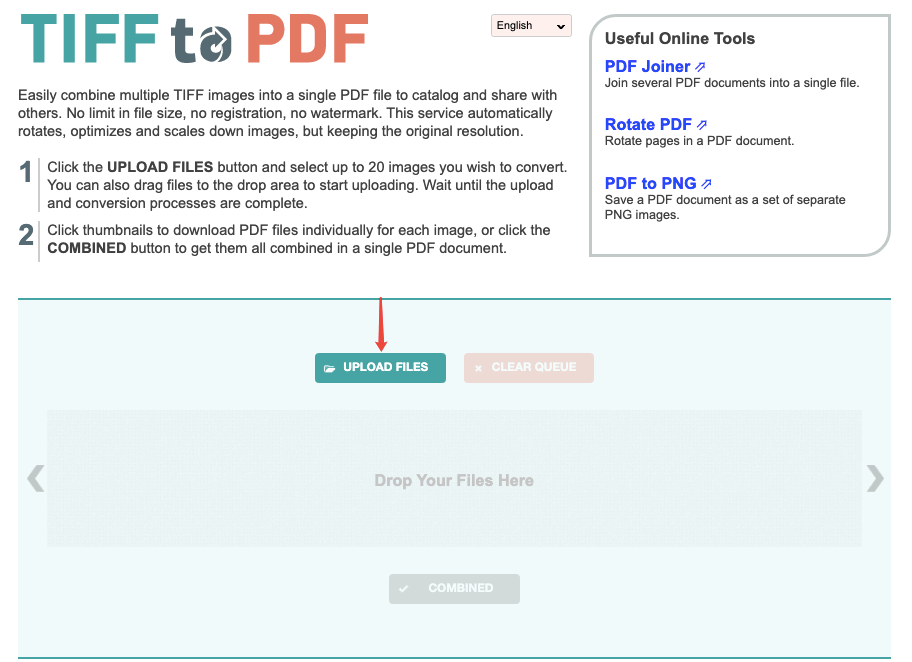 Authors should label each raw blot or gel image to clearly annotate the loading order, identity of experimental samples, method used to capture the image, and to specify which figure panel was generated from that original image. The file should be named ‘S1_raw_images’ and uploaded as a Supporting Information file or deposited at a suitable publicly-available data repository, with the dataset identifier (DOI or other form of persistent identifier) provided in the Data Availability Statement. We do not recommend compiling the images in Powerpoint as resolution can be lost.
Authors should label each raw blot or gel image to clearly annotate the loading order, identity of experimental samples, method used to capture the image, and to specify which figure panel was generated from that original image. The file should be named ‘S1_raw_images’ and uploaded as a Supporting Information file or deposited at a suitable publicly-available data repository, with the dataset identifier (DOI or other form of persistent identifier) provided in the Data Availability Statement. We do not recommend compiling the images in Powerpoint as resolution can be lost. You could also use a PDF program to build a single PDF compiled from multiple annotated jpeg/tiff image files. Gimp, Photoshop) to compile and annotate the original images and then exporting/saving as a tiff file with LZW compression.
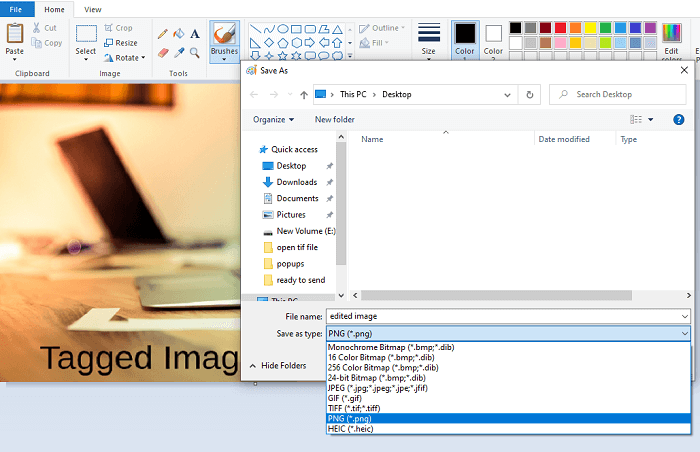
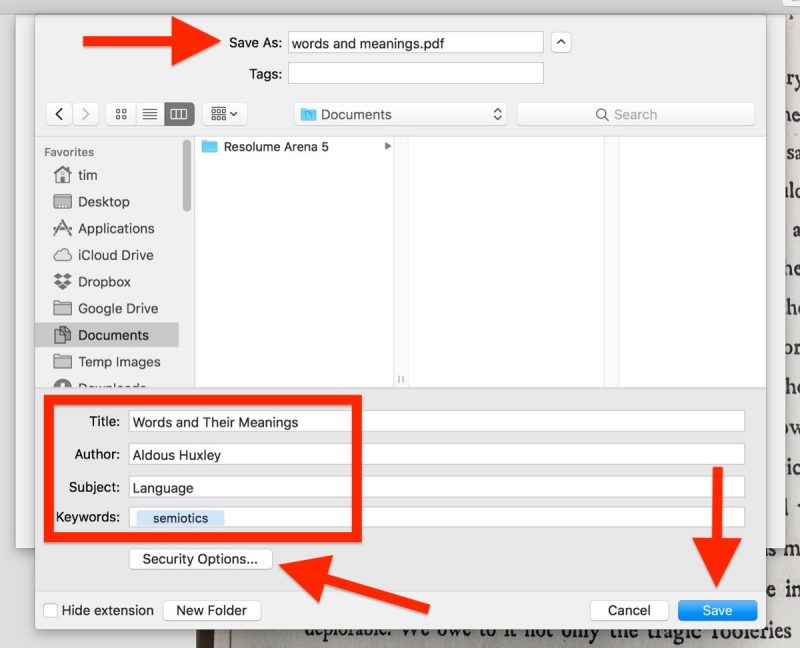
Please create a single PDF file that contains all the original blot and gel images contained in the manuscript’s main figures and supplemental figures. Please follow these instructions when preparing and submitting blot/gel data files: Whilst it is not necessary to provide original images at time of initial submission, we will require these files during the peer review process or before a manuscript can be accepted. If you have questions about these requirements please email us at Original images for blots and gelsĪuthors must provide the original, uncropped and minimally adjusted images supporting all blot and gel results reported in an article’s figures and supporting information files. The figure preparation guidelines that follow clarify PLOS ONE standards and requirements, and aim to ensure the integrity and scientific validity of blot/gel data reporting. The original images also provide additional information for readers about background within the experiment and the specificity of reagents used. The underlying data requirement is in place to ensure that the results are reported in a fully transparent manner, and that readers can verify results by reviewing the primary data in its original form. Each TIFF file begins with an image file header which then points to an image file directory which contains the image data and image information.The following requirements apply to any figures and supporting Information files that report blot or gel data. if it is MM, then you have Motorola byte ordering and likewise if it is II it means you have Intel byte ordering. The byte order is either Motorola or Intel depending on the first word. It is a popular format for high-colour-depth images and it has also been adapted to accommodate greyscale images.Ī TIFF file is made up of many different blocks which define the palette data or the LZW-compressed body among other things. It was created due to the popularity of scanners and was thought-up to become the standard scanned image file format. Tiff was originally created by a company called Aldus, and is now owned by Adobe systems, it is a file format for storing images, including line art and photographs. Microsoft Office binary file format specifications. Free alternatives to Microsoft to open doc files. doc files can also contain mail merge information, which allows a word-processed template to be used in conjunction with a spreadsheet or database. As PC technology has grown the original uses for the extension have become less important and have largely disappeared from the PC world.Įarly versions of the doc file format contained mostly formatted text, however development of the format has allowed doc files to contain a wide variety of embedded objects such as charts and tables from other applications as well as media such as videos, images, sounds and diagrams. It was in the 1990s that Microsoft chose the doc extension for their proprietary Microsoft Word processing formats.
Almost everyone would have used the doc file format, whenever you write a letter, do some work or generally write on your PC you will use the doc file format.
Historically, it was used for documentation in plain-text format, particularly of programs or computer hardware, on a wide range of operating systems. Doc (an abbreviation of document) is a file extension for word processing documents it is associated mainly with Microsoft and their Microsoft Word application.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
